
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information and Sensing Technologies of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Department of Optoelectronic Engineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications, Department of Optoelectronic Engineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
3 Center for Information Photonics and Communications, School of Information Science and Technology, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 611756, China
Temperature sensing is essential for human health monitoring. High-sensitivity () fiber sensors always require long interference paths and temperature-sensitive materials, leading to a long sensor and thus slow response (6–14 s). To date, it is still challenging for a fiber optic temperature sensor to have an ultrafast () response simultaneously with high sensitivity. Here, a side-polished single-mode/hollow/single-mode fiber (SP-SHSF) structure is proposed to meet the challenge by using the length-independent sensitivity of an anti-resonant reflecting optical waveguide mechanism. With a polydimethylsiloxane filled sub-nanoliter volume cavity in the SP-SHSF, the SP-SHSF exhibits a high temperature sensitivity of 4.223 nm/°C with a compact length of 1.6 mm, allowing an ultrafast response (16 ms) and fast recovery time (176 ms). The figure of merit (FOM), defined as the absolute ratio of sensitivity to response time, is proposed to assess the comprehensive performance of the sensor. The FOM of the proposed sensor reaches up to , which is more than two to three orders of magnitude higher than those of other temperature fiber optic sensors reported previously. Additionally, a three-month cycle test shows that the sensor is highly robust, with excellent reversibility and accuracy, allowing it to be incorporated with a wearable face mask for detecting temperature changes during human breathing. The high FOM and high stability of the proposed sensing fiber structure provide an excellent opportunity to develop both ultrafast and highly sensitive fiber optic sensors for wearable respiratory monitoring and contactless in vitro detection.
Photonics Research
2023, 11(8): 1397
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information and Sensing Technologies of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Department of Optoelectronic Engineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2 Engineering Research Center on Visible Light Communication of Guangdong Province, Department of Optoelectronic Engineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
3 Key Laboratory of Visible Light Communications of Guangzhou, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
Side polished fiber (SPF) has a controllable average roughness and length of the side-polishing region, which becomes a versatile platform for integrating multiple materials to interact with the evanescent field to fabricate all-fiber devices and sensors. It has been widely used in couplers, filters, polarizers, optical attenuators, photodetectors, modulators, and sensors for temperature, humidity, strain, biological molecules, chemical gas, and vector magnetic monitoring. In this article, an overview of the development history, fabrication techniques, fiber types, transmission characteristics, and varied recent applications of SPFs are reviewed. Firstly, the fabrication techniques of SPFs are reviewed, including the V-groove assisted polishing technique and wheel polishing technique. Then, the different types of SPFs and their characteristics are discussed. Finally, various applications of SPFs are discussed and concluded theoretically and experimentally, including their principles and structures. When designing the device, the residual thickness and polishing lengths of the SPF need to be appropriately selected in order to obtain the best performance. Developing all-fiber devices and sensors is aimed at practical usability under harsh environments and allows to avoid the high coupling loss between optical fibers and on-chip integrated devices.
Side polished fiber (SPF) V-groove assisted polishing technique wheel polishing technique lab-on-fiber fiber devices sensors Photonic Sensors
2023, 13(1): 230120
1 暨南大学光电工程系广东省高等院校光电信息与传感技术重点实验室, 广东 广州 510632
2 广东技术师范大学电子与信息学院, 广东 广州 510632
3 暨南大学光电工程系广东省可见光通信工程研究中心, 广东 广州 510632
4 暨南大学广州可见光通信重点实验室, 广东 广州 510632
当前, 光电子器件正朝着微型化和集成化方向发展, 而传统的光电子器件通常基于硅晶片技术或者波导技术, 这就使得芯片需要通过波导模式转换器才能与光纤尾纤进行耦合,因此发展与光纤系统兼容的光电子器件具有重要的现实意义。“光纤实验室” 技术的发展,推动了低维材料与光纤的结合, 促进了光子芯片在光纤上的集成与发展, 有助于开发新一代小型化、集成化、轻量级、低成本、多功能的全光纤光子集成平台。根据光与物质相互作用方式的不同, 光纤集成光电探测器可分为沿波导方向集成和光纤端面集成两种类型。本综述主要回顾了近年来这两类光纤集成光电探测器的制备方法和研究进展, 并对利用光纤作为光电子器件的集成平台的未来发展进行了展望。
光纤通信 光纤集成 二维材料 光电探测器 optical fiber communication optical fiber integration 2D materials photodetectors
1 暨南大学理工学院光电工程系, 广东 广州 510632
2 暨南大学广东省光纤传感与通信技术重点实验室, 广东 广州 510632
石英增强光声光谱(QEPAS)技术是近年来发展迅速的一种气体检测技术,具有灵敏度高、设备体积小、对环境噪声免疫等优点。本课题组设计了一种光纤耦合的全固态中红外QEPAS光声探测模块,并基于气体热动力学和一维声学谐振腔理论,利用COMSOL软件对探测模块的声压分布及声压级进行了研究;然后设计并加工了光机电一体化探测模块,将声学谐振腔、光声池、光纤模块和前置放大模块集成一体,使该模块具有易于准直、稳定性高、抗干扰能力强等特点。采用中心波长为2 μm的高功率中红外分布反馈式激光器,结合波长调制技术,对CO2进行了探测,结果表明,在1 s的积分时间下获得了3.7×10 -5的探测极限。通过Allan方差分析发现,积分时间为1123 s时,系统的探测极限可以达到1.34×10 -6。采用基于该模块的QEPAS系统可以实现对室内CO2浓度的实时监测。
光谱学 石英增强光声光谱 光声光谱 音叉式石英晶振 光声探测模块 光学学报
2021, 41(20): 2030001
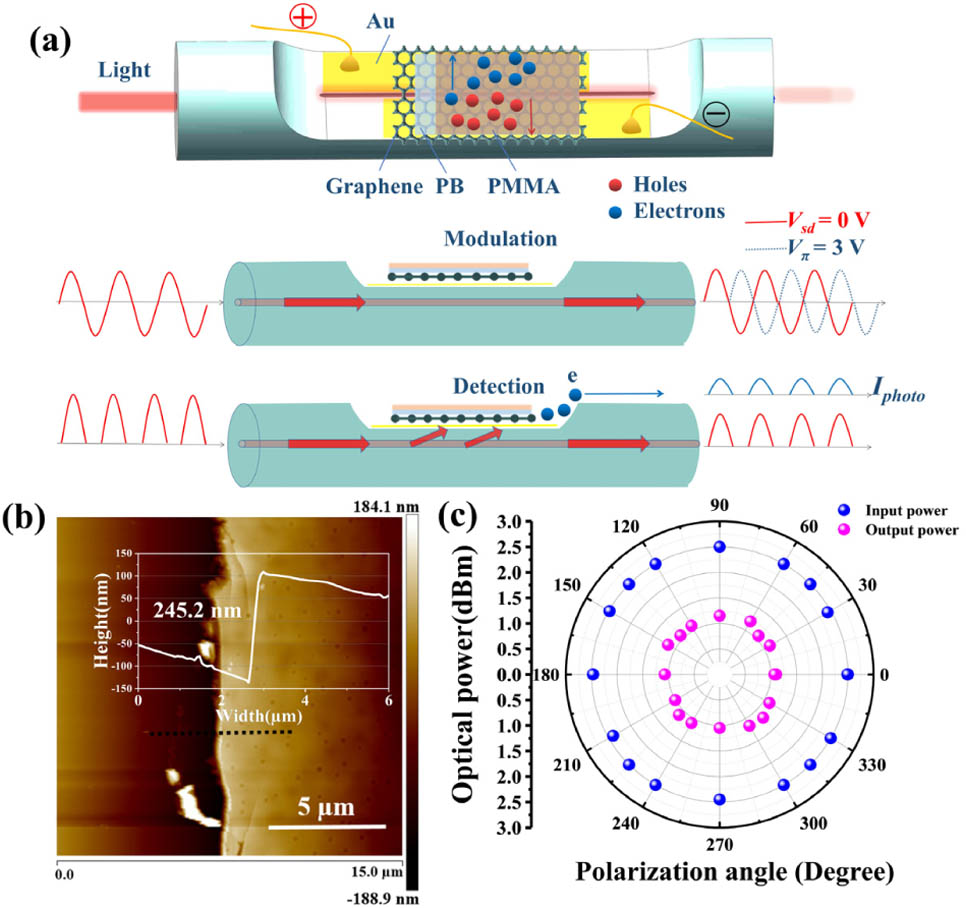
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information and Sensing Technologies of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Department of Optoelectronic Engineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2 Engineering Research Center on Visible Light Communication of Guangdong Province, Department of Optoelectronic Engineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
3 Key Laboratory of Visible Light Communications of Guangzhou, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
4 Science and Technology on Reliability Physics and Application of Electronic Component Laboratory, China Electronic Product Reliability and Environmental Testing Research Institute, Guangzhou 510610, China
5 e-mail: zhuwg88@163.com
In graphene-based optoelectronic devices, the ultraweak interaction between a light and monolayer graphene leads to low optical absorption and low responsivity for the photodetectors and relative high half-wave voltage for the phase modulator. Here, an integration of the monolayer graphene onto the side-polished optical fiber is demonstrated, which is capable of providing a cost-effective strategy to enhance the light–graphene interaction, allowing us to obtain a highly efficient optical absorption in graphene and achieve multifunctions: photodetection and optical phase modulation. As a photodetector, the device has ultrahigh responsivity () and high external quantum efficiency (). Additionally, the polybutadiene/polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) film on the graphene can render the device an optical phase modulator through the large thermo-optic effect of the PMMA. As a phase modulator, the device has a relatively low half-wave voltage of 3 V with a 16 dB extinction ratio in Mach–Zehnder interferometer configuration.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(12): 12001949
1 暨南大学 光电工程系, 广东 广州 510632
2 广东省可见光通信工程技术研究中心, 广东 广州 510632
3 广州市可见光通信工程技术重点实验室, 广东 广州 510632
室内停车场是静态交通的一个重要组成部分, 由于缺乏有效的室内定位技术, 目前存在着泊车导航以及反向寻车困难的问题。提出一种基于LED照明灯光的可见光室内停车场定位导航系统, 实现了面向车辆的停车位引导和面向行人的反向寻车导航, 具有定位速度快、定位精度高和"照明定位两用"的优势。实验结果及现场测试表明: 该系统定位精度可达到7.5 cm, 可支持车辆或行人在时速达17 km/h下的实时定位导航。
可见光通信 停车系统 室内定位 LED照明定位两用灯 visible light communication parking system indoor positioning LED lighting and positioning dual use

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2 Department of Optoelectronic Engineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
3 School of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Foshan University, Foshan 528000, China
4 e-mail: kensomyu@gmail.com
Tiny but universal beam shifts occur when a polarized light beam is reflected upon a planar interface. Although the beam shifts of Gaussian beams have been measured by the weak measurement technique, the weak measurement for orbital angular momentum (OAM)-induced spatial shifts of vortex beams is still missing. Here, by elaborately choosing the preselection and postselection states, the tiny OAM-induced Goos–H nchen and Imbert–Fedorov shifts are amplified at an air–prism interface. The maximum shifts along directions both parallel and perpendicular to the incident plane are theoretically predicted and experimentally verified with optimal preselection and postselection states. These maximum shifts can be used to determine the OAM of vortex beams.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(11): 11001273

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications, Department of Optoelectronic Engineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information and Sensing Technologies of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
3 e-mail: qiuwentao@jnu.edu.cn
4 e-mail: ttguanheyuan@jnu.edu.cn
An all-optical light–control–light functionality with the structure of a microfiber knot resonator (MKR) coated with tin disulfide () nanosheets is experimentally demonstrated. The evanescent light in the MKR [with a resonance of and an extinction ratio (ER) of ] is exploited to enhance light–matter interaction by coating a two-dimensional material nanosheet onto it. Thanks to the enhanced light–matter interaction and the strong absorption property of , the transmitted optical power can be tuned quasi-linearly with an external violet pump light power, where a transmitted optical power variation rate with respect to the violet light power of is obtained. In addition, the MKR structure possessing multiple resonances enables a direct experimental demonstration of the relationship between resonance properties (such as and ER), and the obtained variation rate with respect to the violet light power. It verifies experimentally that a higher resonance and a larger ER can lead to a higher variation rate. In terms of the operating speed, this device runs as fast as . This kind of all-optical light–control–light functional structure may find applications in future all-optical circuitry, handheld fiber sensors, etc.
Photonics Research
2018, 6(12): 12001137
1 暨南大学 广州可见光通信工程技术研究中心,广东 广州510632
2 暨南大学 广东高校光电信息与传感技术重点实验室,广东 广州510632
3 暨南大学 广州可见光通信重点实验室, 广东 广州510632
4 暨南大学 理工学院 光电工程系, 广东 广州510632
在复杂光照条件下二维码扫码器采集到的图像容易出现整体高亮、阴影区域和局部高亮、阴影区域, 使得图像分割阈值确定困难, 研究了Sauvola算法中的窗口大小w值和修正因子k值对于QR码图像二值化的影响。针对全局二值化方法抗噪能力差和局部二值化方法处理速度慢的缺陷, 提出了一种改进的QR码图像二值化方法, 将Otsu和Sauvola算法相结合提升算法抗噪能力, 并利用积分图算法提高算法运行效率。实验证明, 该方法二值化效果优于经典的二值化方法, 平均运行效率比原Sauvola算法提高17倍, 提升了识别成功率。
QR码 二值化 修正因子 积分图像 QR code binarization correction factor integral image
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information and Sensing Technologies of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes,Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2 Department of Optoelectronic Engineering, Jinan University,Guangzhou 510632, China
3 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China





